Abstract
Background The Canadian TKI discontinuation (TRAD) trial (NCT02268370) has evaluated whether Dasatinib (DA) rechallenge can sustain a second treatment-free remission (TFR2) after failure of Imatinib (IM) discontinuation (DISC) for the first TFR (TFR1) attempt. We previously reported that: 1) The 12-month molecular relapse-free survival (mRFS) rate for TFR1 is 58.0%; 2) Re-challenge with DA following TFR1 failure after IM DISC restores deep molecular response (MR) quickly; 3) 12 months DA rechallenge does not significantly improve TFR2 rate (EHA 2022). The clinical risk factors associated with TRF2 failure are evaluated in this study.
Patients and Methods This prospective study (BMS CA180-543, NCT#02268370) had 3 phases: 1) IM discontinuation for TFR1, 2) DA rechallenge, and 3) DA discontinuation for TFR2. Key inclusion criteria included: 1) CML in chronic phase, 2) minimum duration of IM therapy 3 years, 3) minimum duration of MR4.5 or deeper over 2 years. Molecular relapse was defined as an increase BCR::ABL qPCR >MR4 on 2 consecutive occasions, or a single increase in BCR::ABL qPCR >MR3. DA treatment was started at 100mg daily after molecular relapse was confirmed, and continued for at least 12 months after achieving ≥MR4 until TFR2 is attempted. Molecular relapse-free survival (RFS) after DA discontinuation was calculated and analyzed according to the risk factors.
Results With a median follow-up duration of 27.5 months (range 1.8-51), in the TFR2 phase, 35 pts stopped DA for a TFR2. Only 3 of 35 pts (8.6%), maintained the MR at last follow-up, the remaining 32 lost the MR within a median 3.65 months. The actuarial mRFS rate at 6 and 12 months was 22.9% (95% CI, 10.8-37.6%) and 10.0% (2.7-23.1%).
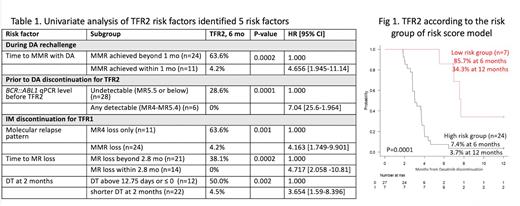
Potential risk factors for TFR2 from three different phases were evaluated, and 5 were found to be associated with TFR2 failure in univariate analysis (table 1):
1. In the DA rechallenge phase, failure to achieve MMR in less than 1 month with DA rechallenge increased the risk of TFR2 failure, in comparison to those who achieved MMR in less than a month (HR 4.656, p=0.0002).
2. Prior to DA DISC phase, any detectable BCR::ABL1 qPCR level between MR4 to MR5.4 showed an increased risk of TFR2 failure, compared to undetectable BCR::ABL1 qPCR level below MR5.5 (HR 4.04, p=0.0001).
3. Among the variables during the IM DISC phase:
4. Molecular relapse pattern: in comparison to the loss of MR4 only, those who lost MMR had an increased risk of TFR2 failure (HR 4.163, p= 0.001).
5. Time to loss of MR within 2.8 months after IM DISC increased the risk of TFR2 failure, in comparison who lost MR beyond 2.8 months (HR 4.717, p=0.0002).
6. Shorter doubling time (DT) at 2 months below 12.75 days and above 0 increased the risk of TFR2 failure, compared to DT at 2 months above 12.75 days or below 0 (HR 654, p=0.002)
Multivariate analysis was performed to identify independent risk factors, identifying 3 clinical factors predictive of TFR2 failure: 1) Failure to achieve MMR in less than 1 month following DA rechallenge (p=0.007, HR 9.542 [1.819-50]); 2) DT below 12.75 days at 2 months after IM DISC (p=0.015, HR 4.368 [1.334-14.30]); and 3) any detectable BCR::ABL1 transcript level between MR4 and MR5.4 before DA DISC (p=0.047, HR 2.759 [1.014-7.513]). A risk score model was generated incorporating these 3 clinical risk factors. A score of 1 was assigned to each one of these risk factors. The group with a score of 0 vs 1-3 was labeled as low vs high-risk, respectively. The low-risk group (n=7) showed 85.7% and 34.3% of TFR2 rate at 6 and 12 months, while the high-risk group (n=24) showed 7.4% and 3.7% of TFR2 rate at 6 and 12 months, (p=0.0003; HR 6.518 [2.219-19.95] for high-risk group vs low risk; Figure 1).
Conclusion As we have previously reported, DA treatment rarely achieves a sustained TFR2 after failing the first IM DISC attempt. However, our current result suggests that TFR2 attempt can be successful in a selected group of patients if: 1) Rapid reduction of initial molecular kinetics is achieved within 1 month of DA rechallenge, 2) an undetectable BCR::ABL1 qPCR level is reached before TFR2 attempt 3) longer doubling time at 2 months after IM DISC is noted. The proposed risk model can be used as a predictive tool for TFR2 failure. Further studies to improve TFR2 rate should investigate the addition of new therapies and consider the use of innovative tools with higher precision and sensitivity to quantify the MR.
Disclosures
Perusini:Pfizer: Consultancy. Busque:Novartis: Consultancy. Xenocostas:Novartis: Honoraria. Leber:Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AMGEN: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Kim:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Paladin: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal